Mamba-based Approximate Conformance Checking Method
What sparks might fly when the latest 2024 advancements in neural networks are applied to conformance checking?
The use of neural networks in process mining is not new, however, the application of neural networks in conformance checking has been underexplored. Mamba is a new 2024 state-space model that can achieve longer context memory than RNN, but is more efficient than Transformer, especially in scenarios where process structures are unknown and the system logs are large-scale. In this study, we propose an Mamba-based approximate conformance checking method MACC, which based on Mamba classifiers and Temporal Convolutional Networks (TCNs) that significantly improves the efficiency of fitness approximation. While maintaining fitness values that are almost identical to the actual values, our approach substantially reduces computation time.
The proposed MACC method achieves approximate conformance checking through a two-stage training process:

Stage 1: Classifier Training
- Log Mutation: The event log is mutated to generate both correct (fitness = 1) and incorrect (fitness < 1) traces.
- Fitness Computation: The pm4py library is used to compute the fitness values of each trace via alignment techniques. Traces with a fitness value of less than 1 are labeled as 0, while others are labeled as 1.
- Split-Bucket Strategy: Based on the length distribution of the traces, the log is divided into three buckets using a normal distribution-based binning strategy. Each bucket is used to train a dedicated Mamba classifier. The strategy is helpful to solve sparse coding problems for long traces.
Stage 2: Regressor Training
- Feature Embedding: The embeddings produced by the classifier in Stage 1 are combined with the original trace embeddings.
- Training the Regressor: These enhanced embeddings are used alongside the original fitness values to train a regressor, improving the accuracy of fitness predictions.
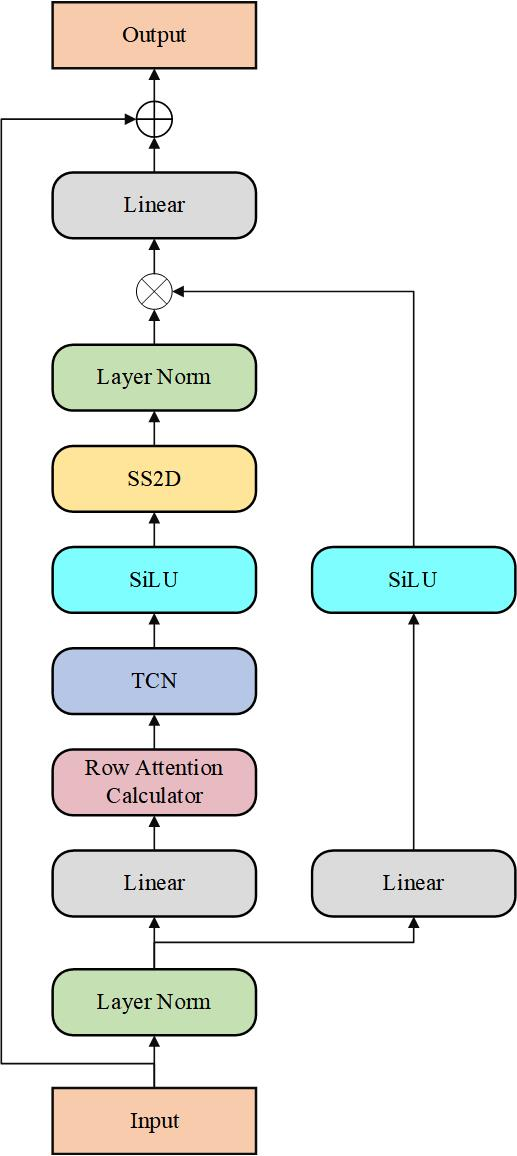
Our classifier leverages a Mamba-based architecture designed for efficient feature extraction. It incorporates layer normalization, row attention (RA) for capturing sequence correlations, and Temporal Convolutional Networks (TCN) for fine-grained temporal feature mining. The structure of our proposed classifier as follows: